![]()
The Dual Faces of Cerium Nitrate: Weighing its Advantages and Disadvantages
In the bustling world of industrial and scientific endeavors, Cerium Nitrate emerges as a compound of paramount importance. As suppliers of this versatile chemical, Shandong Honrel Ltd. navigates you through the intricacies of Cerium Nitrate, shedding light on both its strengths and limitations. This exploration aims to offer a balanced perspective, empowering you with knowledge to leverage Cerium Nitrate’s benefits while mitigating its potential downsides.
Table of Contents
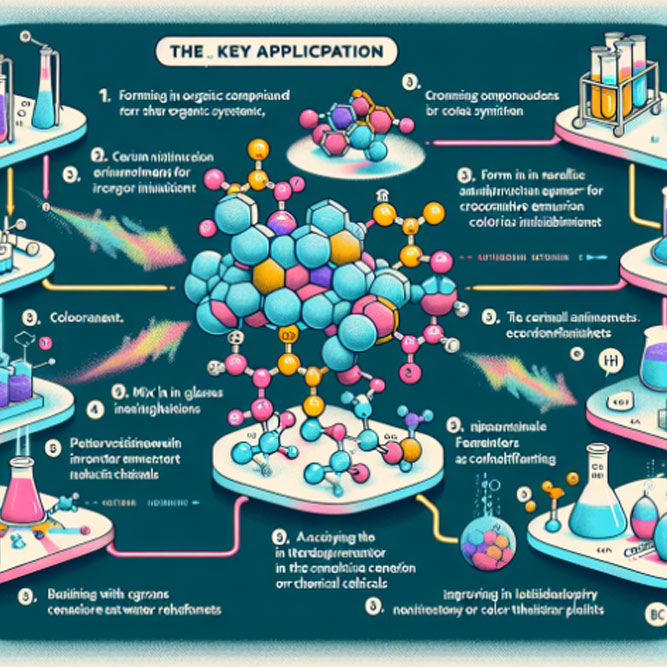
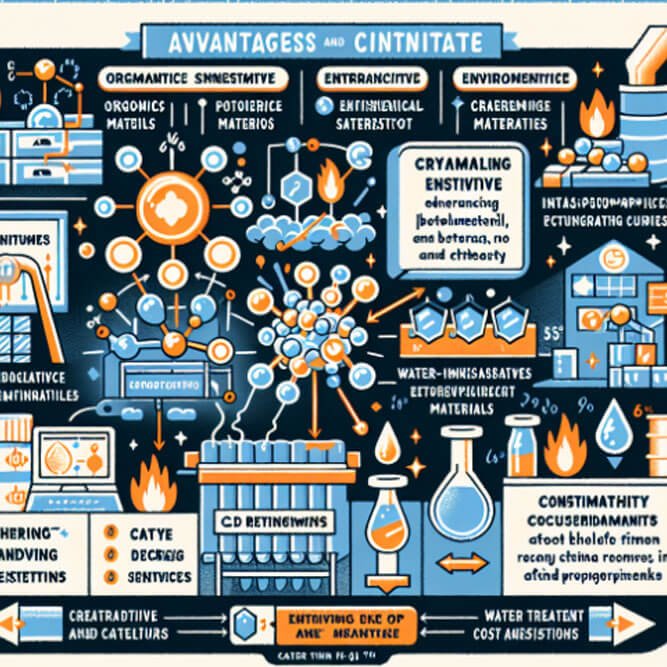
Advantages of Cerium Nitrate
A Catalyst for Innovation in Organic Synthesis
Cerium Nitrate stands out as a powerful catalyst in organic synthesis processes. Its ability to streamline complex chemical reactions without requiring excessively harsh conditions is a game-changer. This not only makes synthesis more efficient but also contributes to the development of new methodologies in organic chemistry, opening doors to novel compounds and therapeutics.
Enhancer of Photoluminescent Materials
The application of Cerium Nitrate in the production of photoluminescent materials is nothing short of revolutionary. By facilitating the creation of glow-in-the-dark products with enhanced brightness and longevity, it plays a crucial role in safety signage, display technologies, and beyond. This not only enhances product quality but also contributes significantly to safety and innovation in various fields.
An Ally in Corrosion Protection
Cerium Nitrate’s role in corrosion inhibition cannot be overstated. Its application on metal surfaces forms a protective layer, vastly extending the lifespan of structures and machinery. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in industries where durability and reliability are paramount, such as in construction and automotive manufacturing.
Purity in Water Treatment
In the realm of environmental sustainability, Cerium Nitrate shines in water treatment technologies. It aids in the removal of pollutants and pathogens, ensuring access to clean and safe water. This advantage is crucial in combating waterborne diseases and promoting public health, showcasing CeriumNitrate’s role in fostering a healthier environment.
Disadvantages of Cerium Nitrate
Handling Sensitivity
The hygroscopic nature of Cerium Nitrate necessitates careful handling and storage conditions. Its propensity to absorb moisture can lead to clumping or degradation, which may impair its effectiveness or pose challenges in industrial applications. This sensitivity underscores the need for meticulous storage solutions and protocols.
Environmental Considerations
While Cerium Nitrate contributes positively to environmental efforts through water treatment, its disposal raises concerns. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination, affecting ecosystems and water sources. Thus, it emphasizes the importance of responsible waste management practices to mitigate potential negative impacts.
Reactivity and Safety Hazards
Cerium Nitrate’s reactive nature, while beneficial in applications, also poses safety hazards during handling and storage. It may react vigorously with combustible materials or when exposed to heat, necessitating strict safety measures and emergency preparedness to prevent accidents.
Cost Implications
The production and purification of Cerium Nitrate demand sophisticated processes, which may translate to higher costs compared to less reactive alternatives. For industries operating on tight budgets, this might pose a challenge, balancing the unique benefits of Cerium Nitrate against its cost implications.
In Summation
Cerium Nitrate holds a multifaceted role across a plethora of sectors, marked by its impressive advantages and countered by noteworthy disadvantages. As a leading supplier, Shandong Honrel Ltd. is dedicated to providing high-quality Cerium Nitrate while ensuring our clients are well-informed about its use, handling, and disposal. Understanding the dual faces of Cerium Nitrate enables us to harness its full potential responsibly, paving the way for advancements in science, technology, and environmental stewardship.