![]()

Palladium Carbon Catalyst Density
When considering the purchase of a palladium carbon catalyst, it is essential to understand the role of density in the catalyst’s overall performance. Palladium carbon catalysts are widely used in chemical reactions, especially hydrogenation reactions, where they play a pivotal role in converting unsaturated compounds to saturated ones.
This article provides a detailed explanation of palladium carbon catalyst density, the key specifications, factors influencing density, and why it matters for catalyst selection. Additionally, we will dive into Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst product specifications, so you can make an informed decision when choosing your catalyst supplier.
Table of Contents
What is Palladium Carbon Catalyst?
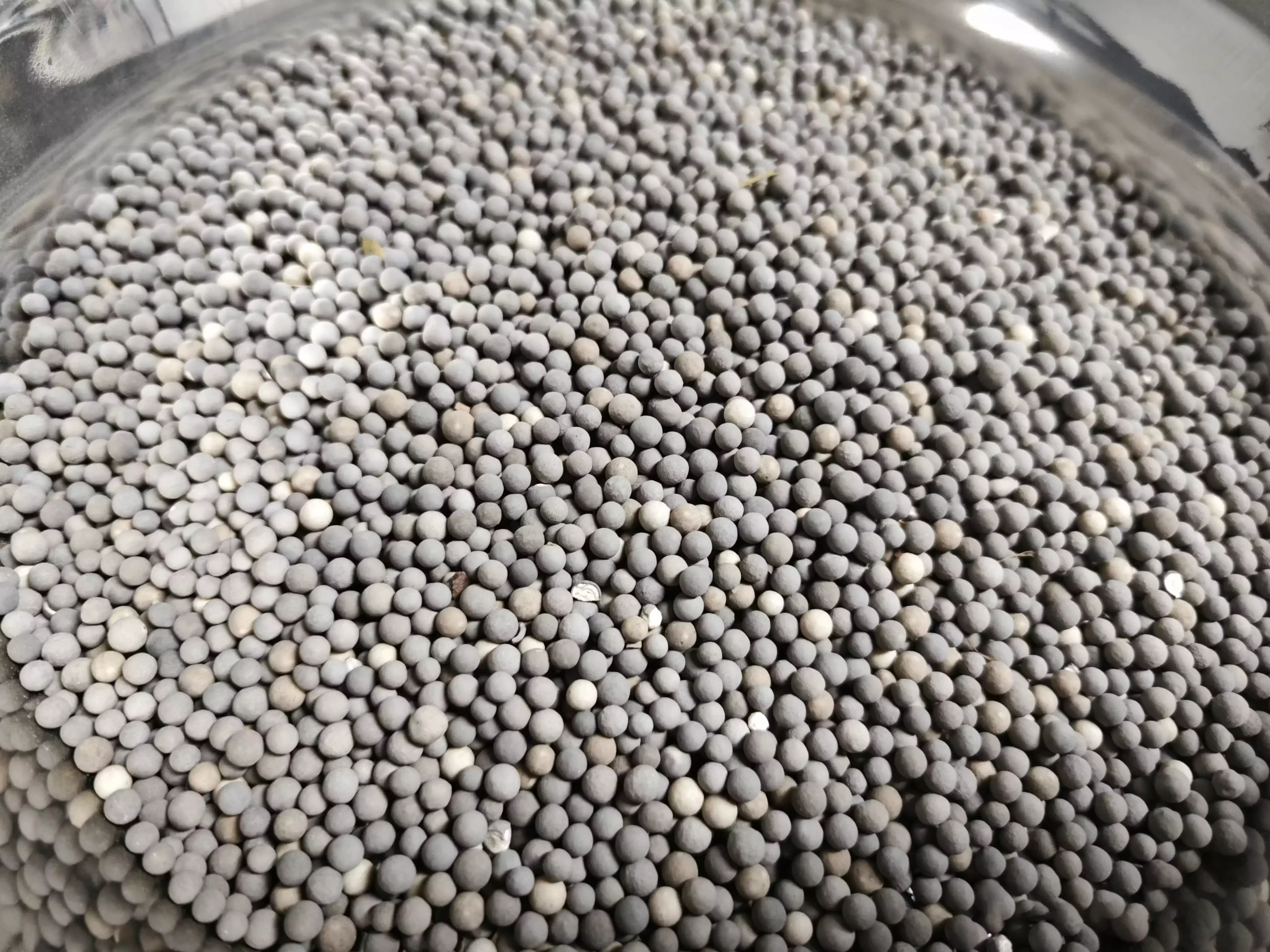
A palladium carbon catalyst consists of palladium (Pd), a precious metal, supported by activated carbon. The palladium content in the catalyst acts as the active site, where hydrogenation reactions occur. These reactions are essential for industries such as pharmaceuticals, biofuels, petrochemicals, and chemical manufacturing.
The catalyst plays an important role in reducing the activation energy required for reactions, making the process faster and more efficient. As palladium is expensive, the use of activated carbon as the support material reduces costs while maintaining high efficiency.
Why is Density Important in Palladium Carbon Catalysts?
Density refers to the mass per unit volume of the catalyst. For palladium carbon catalysts, density influences several key factors:
- Catalytic Activity: The right density ensures that the palladium particles are optimally distributed on the carbon support. This leads to more active sites, which enhances the reaction rate.
- Handling and Transport: Knowing the catalyst’s density helps with storage and transportation. A higher density means that a given volume of catalyst will weigh more, which can affect handling logistics.
- Surface Area and Reactivity: The surface area of the catalyst is inversely related to particle size. A higher density generally means smaller particles, which increases the surface area available for reactions.
Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst Specifications
Honrel provides high-quality palladium carbon catalysts, designed to meet the needs of a variety of industrial applications. Here are the product specifications for Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst:
- CAS No.: 7440-05-3
- Palladium Content: 0.1% ~ 30%
- Carrier Material: Coconut shell, coal, wood, peat, etc.
- Carrier State: Powdered activated carbon
- Specific Surface Area: ≥ 930 m²/g
- Metal Surface Area: 85 ~ 105 m²/g
- Average Particle Size of Carrier: 15, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100 μm (adjustable based on application)
- Impurities: Cu, Fe, Cr, Ni, Ag, Mg, and other impurities ≤ 0.3%
- Particle Strength: ≥ 90%
- Moisture Content: 0.1% ~ 65%
- Ash Content: ≤ 5%
These specifications make Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst suitable for a variety of applications, especially in hydrogenation reactions where high reactivity and sustainability are required.
For more details on this product, you can visit Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst Page.
Understanding the Key Factors Influencing Palladium Carbon Catalyst Density
The density of a palladium carbon catalyst depends on several factors, including:
1. Palladium Content
- Palladium content in the catalyst directly influences the density. Higher palladium content results in higher density, as palladium is a dense material.
- Honrel’s palladium carbon catalyst offers palladium content from 0.1% to 30%, providing flexibility for various applications.
2. Carrier Material
- Carrier material such as coconut shell, coal, and peat affects the overall density of the catalyst. The porosity and structure of the carbon support material determine how much palladium can be loaded, and therefore, influence the catalyst’s density.
- Honrel’s palladium carbon catalyst uses a variety of carrier materials, including coconut shell and coal, to provide optimal density and performance.
3. Preparation Method
- The method used to prepare the catalyst can alter its density. For example, palladium particles may be deposited on the activated carbon through processes like impregnation or precipitation, which can affect the final catalyst’s density.
4. Particle Size
- Particle size affects the packing density and the surface area of the catalyst. Smaller particles generally lead to higher surface area, which increases the catalyst’s efficiency.
- Honrel’s palladium carbon catalysts offer an adjustable particle size range from 15 to 100 μm, allowing customers to select the optimal size for their process.
Impact of Density on Palladium Carbon Catalyst Performance
1. Reactivity
- The density of the catalyst affects the contact between the catalyst and the reactants. Higher density ensures a better distribution of palladium across the surface, which leads to more efficient catalytic reactions.
2. Handling and Transport
- A catalyst with a higher density is heavier and may be more challenging to transport in bulk, but it is more compact and concentrated, which could be advantageous for large-scale operations.
3. Regeneration
- Regeneration is an important process in catalyst management. The density of the catalyst affects how easily it can be regenerated. A higher density might mean the catalyst can be used multiple times without significant degradation in performance.
How Palladium Carbon Catalyst Density Affects Industrial Applications
Chemical Manufacturing
In chemical manufacturing, palladium carbon catalysts are used to enhance hydrogenation reactions. The density of the catalyst influences how effectively it interacts with the reactants, ensuring faster reaction times and higher yields.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, palladium carbon catalysts are used in the hydrogenation of organic molecules to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The density of the catalyst plays a role in determining the reaction rate and selectivity, ensuring that the desired chemical compounds are produced efficiently.
Petrochemical Refining
In petrochemical refining, palladium carbon catalysts are crucial for the hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons. The density of the catalyst affects how well it can process large quantities of hydrocarbons while maintaining high throughput and low waste.
Conclusion
When you purchase palladium carbon catalyst, it is essential to consider density as one of the key properties influencing its performance. The density of the catalyst determines how well it can perform in various reactions, especially in hydrogenation processes. By understanding the relationship between palladium content, carrier material, and density, you can select the right catalyst for your industrial needs.
For high-quality, reliable, and high-density palladium carbon catalysts, visit Honrel’s Palladium Carbon Catalyst Page and learn more about our products and specifications.




