![]()

Tabular Alumina for Refractory Castable
In high-temperature industrial settings, tabular alumina for refractory castable plays a vital role. Known for its density, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, tabular alumina is the preferred choice for applications that require materials to withstand extreme heat and mechanical stress. This guide delves into the properties of tabular alumina, its production process, and its role in refractory castables, offering insights into why it is a trusted solution in sectors like metallurgy, cement, and petrochemicals.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Tabular Alumina for Refractory Castable
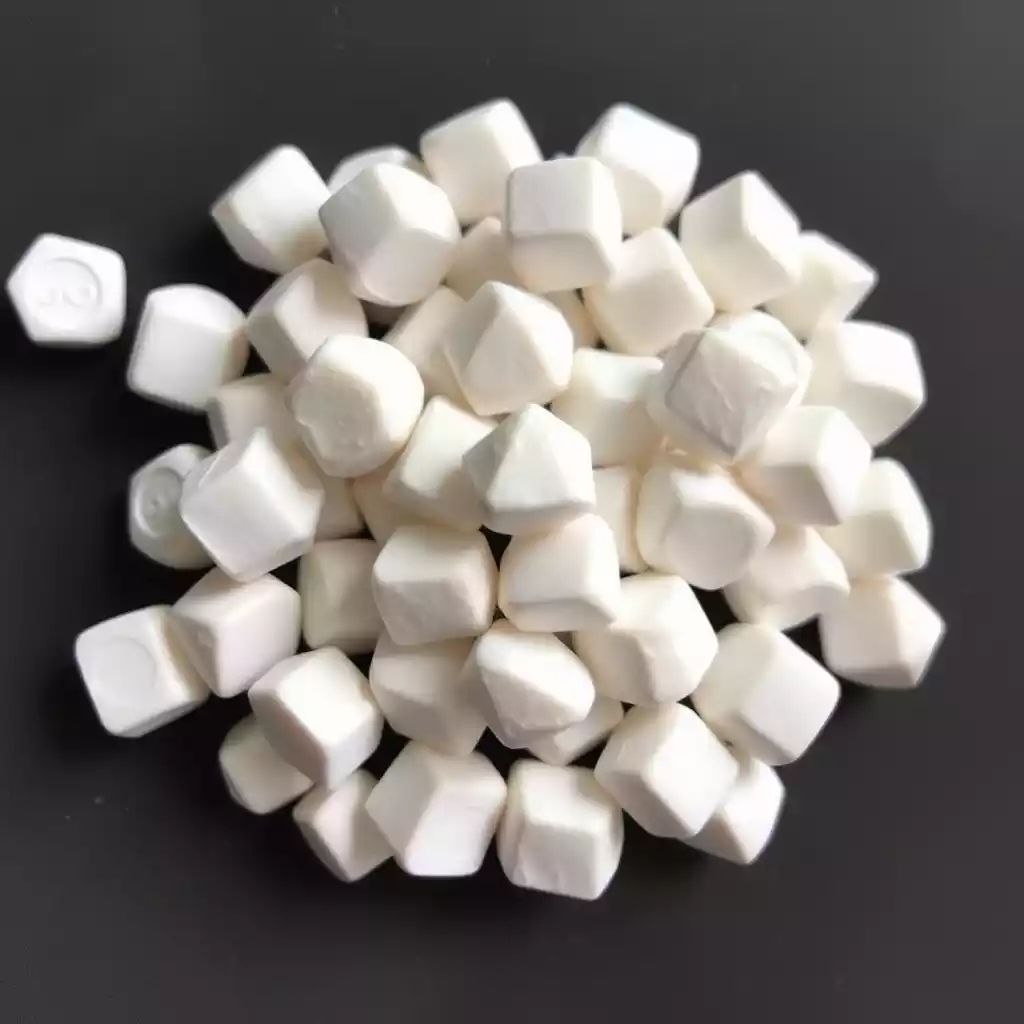
Tabular alumina for refractory castable refers to a high-purity, sintered form of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) that is extensively used to create durable, heat-resistant linings for furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Manufactured through a specialized sintering process, tabular alumina offers the structural integrity needed for castable refractories that encounter severe thermal cycles.
Tabular alumina’s popularity stems from its low porosity, high density, and outstanding resistance to thermal shock. For those seeking robust solutions in high-temperature environments, it provides an unparalleled balance of mechanical strength and thermal stability.
Internal Link Example: For a complete selection of abrasive and refractory materials, explore our catalog.
Image:
High-performance materials for extreme industrial conditions.
Properties and Benefits of Tabular Alumina
Tabular alumina exhibits several properties that make it ideal for use in refractory castables. Here are some of its most notable characteristics:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| High Density | The dense, polycrystalline structure enhances stability and durability under extreme conditions. |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity at high temperatures, crucial for refractory linings in furnaces and kilns. |
| Abrasion Resistance | Withstands mechanical wear, making it suitable for high-stress applications in abrasive settings. |
| Low Porosity | Reduces moisture absorption, improving resistance to thermal shock and chemical attacks. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists reactions with acidic and basic compounds, ideal for challenging chemical environments. |
These properties make tabular alumina a preferred choice for refractory castables that need to handle extreme conditions without compromising structural integrity or performance.
Internal Links:
- Discover our rare earth products for high-quality industrial materials.
- Check out a range of chemical raw materials designed for industrial-grade applications.
Image:
High-quality fused alumina, essential for abrasion-resistant materials.
How Tabular Alumina Is Used in Refractory Castables
- Enhancing Thermal Resistance
The high-density structure of tabular alumina provides superior thermal resistance, reducing the risk of structural degradation under heat stress. When used in castable refractories, it ensures that the refractory linings maintain their shape and durability, even after prolonged exposure to high temperatures. - Improving Mechanical Strength
Tabular alumina enhances the mechanical strength of castable refractories, making them more resilient to mechanical impact and abrasion. This property is crucial in applications that involve frequent loading, unloading, and other forms of mechanical stress. - Reducing Porosity for Longer Lifespan
The low porosity of tabular alumina minimizes moisture absorption and thermal cycling damage, which leads to a longer lifespan for refractory linings. It also helps reduce the need for frequent maintenance, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
Image Example:
Materials essential for high-performance refractory applications.
Internal Link Example: For a reliable source of tabular alumina, explore our product page.
Production Process and Its Impact on Quality
The production of tabular alumina involves several key steps that influence its quality and performance:
- Calcination
Raw alumina is heated to high temperatures, typically around 1000-1100°C, to remove moisture and impurities. This calcination process is the first step toward achieving the high purity that tabular alumina is known for. - Sintering
The calcined alumina undergoes sintering at temperatures around 1800°C. This stage is essential, as it densifies the material and creates a strong, polycrystalline structure with low porosity. - Crushing and Grading
The sintered alumina is then crushed and graded into various sizes, which are tailored for specific industrial applications.
The sintering process gives tabular alumina its characteristic strength and thermal stability, allowing it to meet the demands of industries that require high-performance refractory solutions.
Key Applications of Refractory Castables
Tabular alumina-based refractory castables are used in several high-temperature industries due to their unique properties:
| Application | Role of Tabular Alumina |
|---|---|
| Steel Manufacturing | Essential in furnace linings and ladle insulation, where high temperatures demand maximum thermal stability. |
| Cement Production | Used in kiln linings to improve durability and resistance to wear from chemical and thermal stress. |
| Petrochemical Industries | Provides thermal resistance in high-temperature reactors and processing units, ensuring safe, continuous operation. |
| Glass Manufacturing | Maintains structural integrity in high-temperature glass production environments, where purity and stability are key. |
These applications showcase the versatility and reliability of tabular alumina in environments that require consistent, high-performance materials capable of handling intense conditions.
Internal Link Example: Discover more materials in our abrasive and refractory catalog to meet your specific industrial needs.
FAQs on Tabular Alumina for Refractory Castable
- What makes tabular alumina ideal for refractory castables?
Its high density, low porosity, and thermal stability make it an ideal component in refractory castables, offering superior resistance to thermal and chemical damage. - How is tabular alumina produced?
It is created through high-temperature sintering of calcined alumina, resulting in a dense, durable structure suitable for industrial applications. - Where is tabular alumina used the most?
Steel manufacturing, cement production, and petrochemical industries are among the largest consumers of tabular alumina-based castables due to their demanding environments. - What is the difference between tabular and fused alumina?
Tabular alumina is denser and provides better thermal stability than fused alumina, making it a preferred choice for high-stress, high-temperature applications. - Can I buy tabular alumina in bulk?
Yes, Honrel offers tabular alumina in bulk quantities, ensuring reliable quality and cost-effective solutions for industrial needs.
Conclusion
The durability, thermal stability, and low porosity of tabular alumina for refractory castable make it indispensable in industries that demand high-performance materials. Its role in enhancing refractory castables allows industrial processes to achieve greater efficiency and longevity, even under extreme conditions. For those looking to source reliable, high-quality tabular alumina, Honrel provides a range of solutions tailored to meet the needs of diverse industrial applications.
Visit Honrel to explore our catalog of chemical raw materials, offering comprehensive options that save you time and ensure exceptional quality.